PLEASE NOTE: This test can only be ordered by a healthcare professional. If you suspect you might have aPAP, we encourage you to share this page with your doctor.
Is this lung disease hiding behind common symptoms?
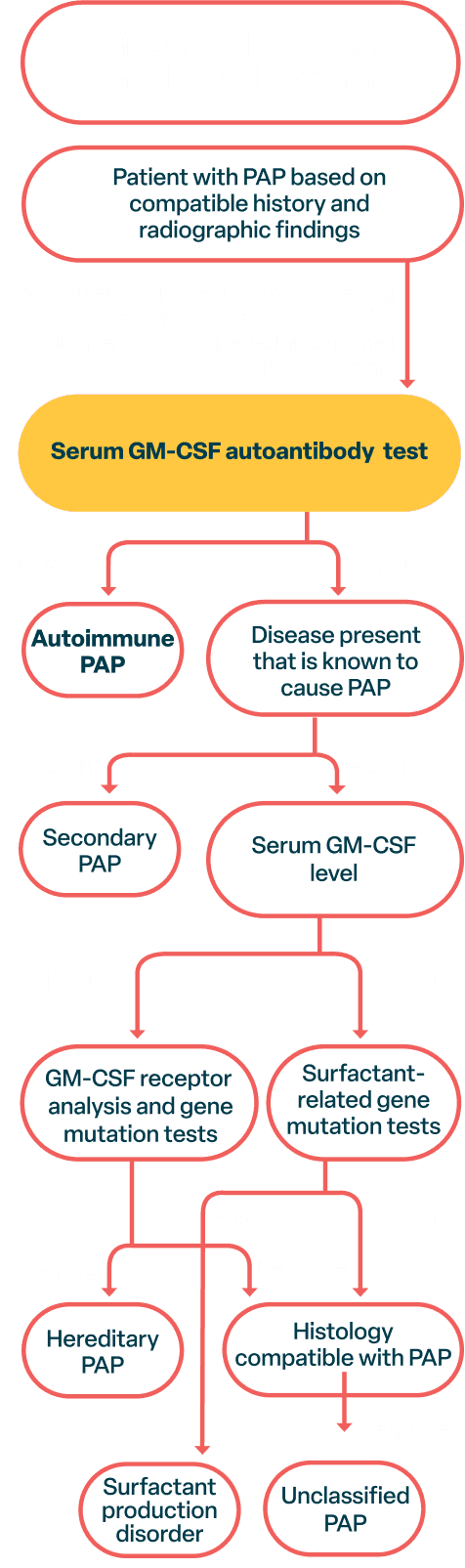
aPAP is a rare lung disease. It is the most common form of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP), accounting for about 90% of PAP cases—but it can be difficult to identify.4
Rare but likely underdiagnosed
In the United States, the prevalence of PAP diagnoses is about 7 in 1 million people. However, because of limited awareness and difficulty in reaching an accurate diagnosis, the true prevalence of PAP is not known.1,5,6
Although symptoms can appear in childhood, most patients are diagnosed in their 30s to 50s. aPAP affects both males and females, with no geographic or racial predominance.4,7,8
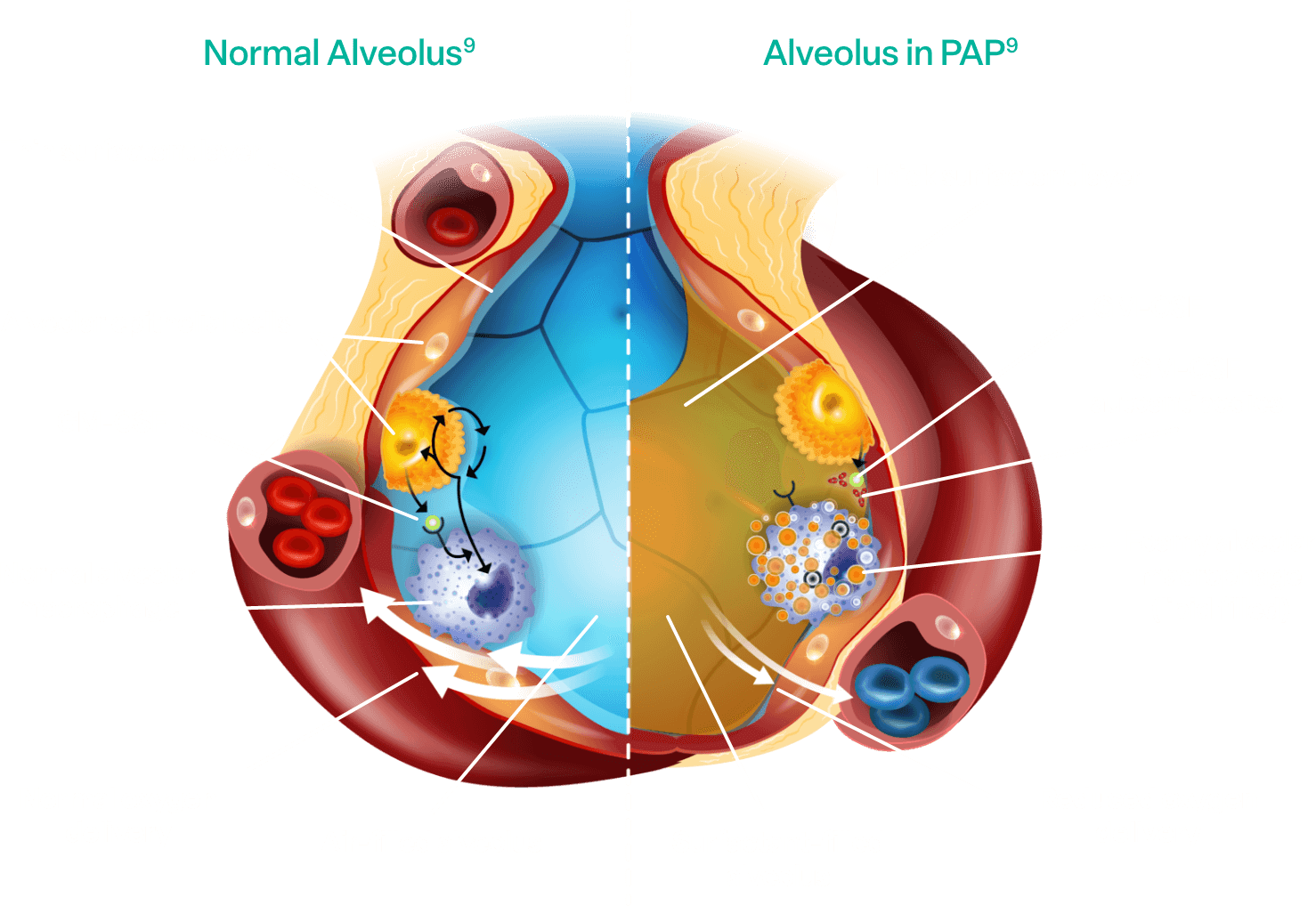
Pathophysiology of aPAP
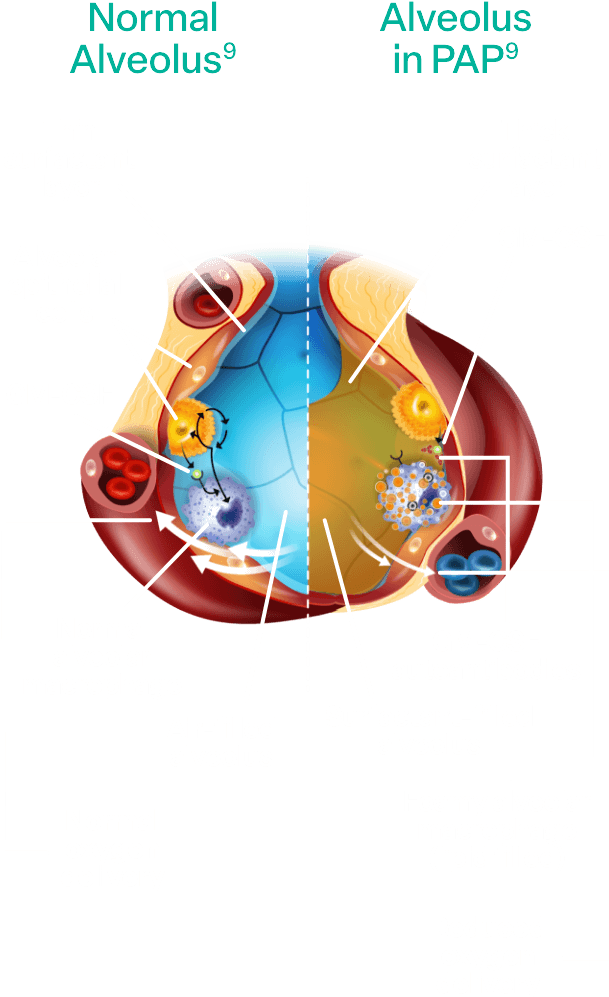
Alveolar macrophages are responsible for clearing surfactant from the alveolar wall. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) is required for alveolar macrophage function and surfactant homeostasis.2,3
In aPAP:
- Autoantibodies interfere with the ability of GM-CSF to bind to alveolar macrophages
- The macrophages are prevented from clearing surfactant in the alveoli2,3
- Surfactant accumulates, impacting gas exchange between the alveoli of the lungs and the blood2,3
When the gas exchange is affected because of aPAP, it can lead to these common symptoms1,2,10,11:

Dyspnea

Chronic cough

Fatigue
Unintentional weight loss

Chest pain
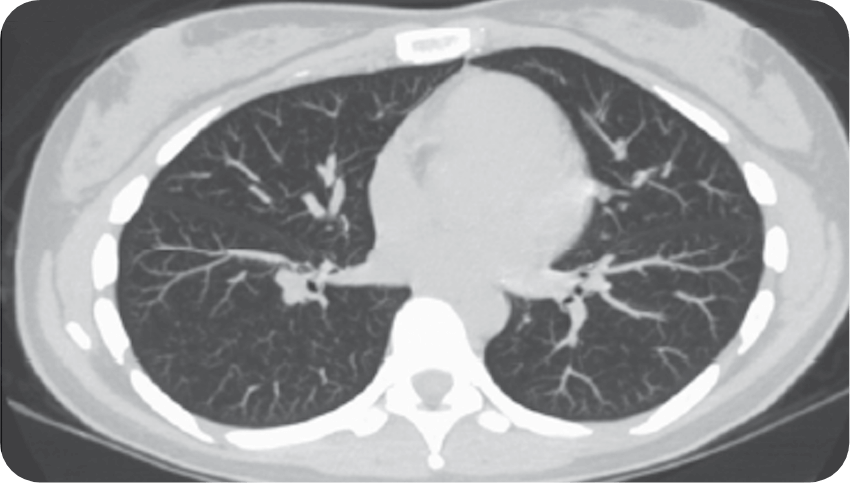
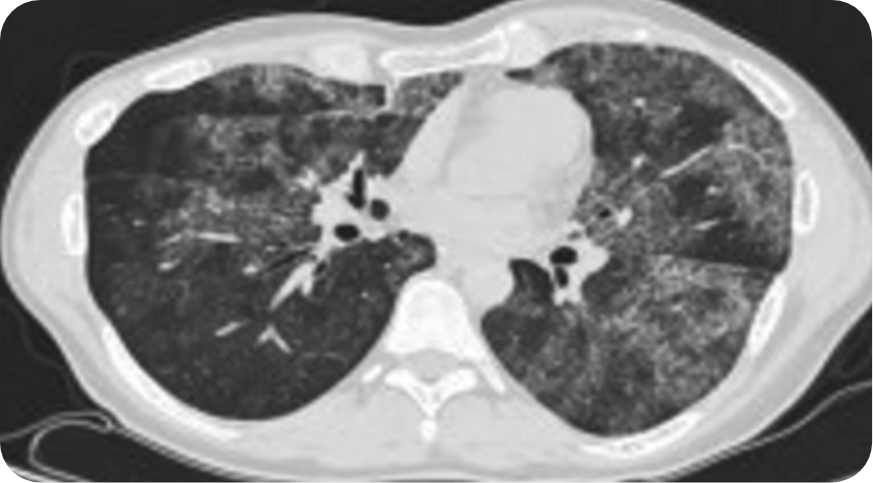
On a computerized tomography (CT) scan, aPAP appears as ground-glass opacification with a crazy-paving pattern—a nonspecific sign with a wide etiology, including infection, pulmonary edema, chronic interstitial disease, and acute alveolar injuries.1,2,10,11
When a patient presents with common symptoms accompanied by an abnormal CT scan, and you suspect pneumonia or other pulmonary diseases, but the patient is not responding to therapy, it's time to test for aPAP.1,2,10,11
One simple, accurate, and noninvasive GM-CSF autoantibody blood test will help you confirm or rule it out.1,2,10,11
Reprinted from Trapnell BC et al. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Nat Rev Dis Primer. 2019;5:16. doi:10.1038/s41572-019-0066-3 with permission from Springer Nature, Copyright © 2019. Available at https://www.nature.com/articles/s41572-019-0066-3
How does undiagnosed aPAP increase clinical burden?
The current diagnostic journey is lengthy. This increases the clinical burden on patients who have to see multiple HCPs and are faced with uncertainty without a definitive diagnosis.11

~18 months of uncertainty3,5,12
It takes an average of 18 months for someone to be diagnosed accurately with aPAP. Patients with aPAP present with symptoms typical of more common pulmonary illnesses—further complicating the diagnosis and often leading to a misdiagnosis.11,13
Misdiagnoses may continue until the failure of multiple courses of therapy prompts diagnostic reconsideration and referral, thereby delaying accurate diagnosis from months to years.11,13
Meanwhile, patients deal with11,13:
- Confusion of a misdiagnosis
- Continued symptoms impacting quality of life
People living with undiagnosed aPAP report that dyspnea and persistent cough disrupt their activities of daily living.11,13
Chronic cough can11:
- Make it difficult to maintain personal relationships
- Hinder performance at work
- Impact mental health and social well-being
When patients are misdiagnosed, they are at risk of inappropriate treatment and poorer outcomes.2
Invasive, nondefinitive tests
The invasive nature of some diagnostic tests disrupts your patient’s daily activities thereby negatively impacting their quality of life. Some procedures, such as bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage and lung biopsy, may require hospitalization.1,11,14
Although these procedures may be helpful in diagnosing PAP, they do not identify the cause of PAP (eg, aPAP).3,4

Confirm or rule out aPAP earlier
Testing for GM-CSF autoantibodies may help you and your patients obtain a definitive diagnosis sooner.1,2
Confirm or rule out aPAP at no cost to you or your patient with the help of a simple, accurate, and noninvasive GM-CSF autoantibody blood test.1,2
PLEASE NOTE: This test can only be ordered by a healthcare professional. If you are a patient, we encourage you to share this page with your doctor.
Could 1 simple test unmask aPAP?
When you see:

Common chronic pulmonary symptoms1,10,11

An abnormal
CT scan1,10,11


Other pulmonary infection diagnoses that are refractory to treatment1,10,11
Then it is time to test for GM-CSF autoantibodies.
Once you suspect aPAP may be causing your patient’s symptoms, request the GM-CSF autoantibody blood test at no cost to you or your patient.2,3
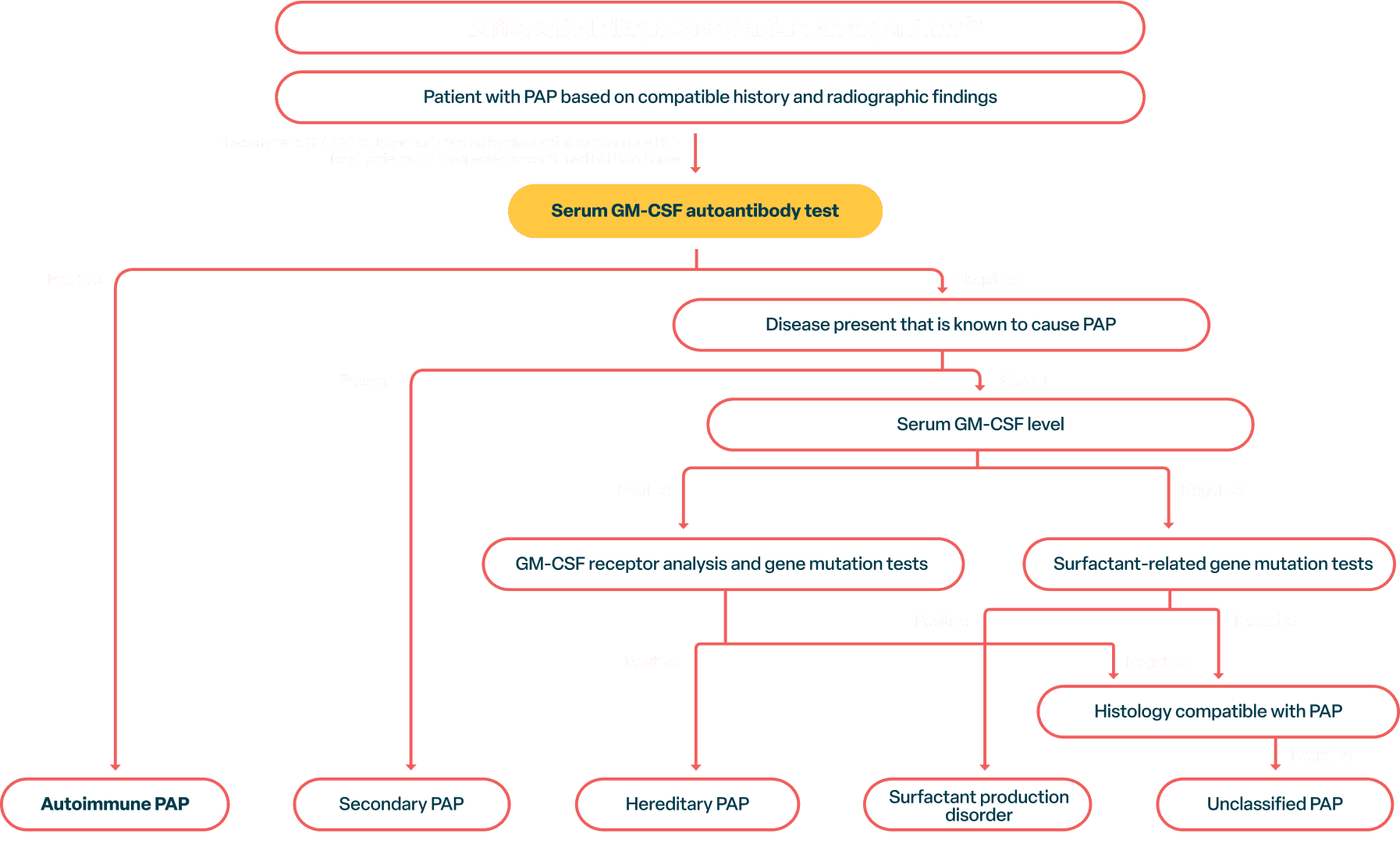
European Respiratory Society Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis. Cormac McCarthy, Francesco Bonella, Marissa O’Callaghan, Clairelyne Dupin, Tiago Alfaro, Markus Fally, Raphael Borie, Ilaria Campo, Vincent Cottin, Aurelie Fabre, Matthias Griese, Alice Hadchouel, Stephane Jouneau, Maria Kokosi, Effrosyni Manali, Helmut Prosch, Bruce C. Trapnell, Marcel Veltkamp, Tisha Wang, Ingrid Toews, Alexander G. Mathioudakis, Elisabeth Bendstrup. Eur Respir J. 2024;14;64(5):2400725. doi:10.1183/13993003.00725-2024
How to test
When diagnosing aPAP, consider a simple and accurate GM-CSF autoantibody blood test instead of an invasive diagnostic bronchoalveolar lavage or a lung biopsy.1-3
Testing for GM-CSF autoantibodies early will not only help you and your patient avoid invasive diagnostic tests, but can also shorten your patient’s diagnostic journey—which may lead to reduced morbidity and lower healthcare costs.1-3

What is the aPAP ClearPath™ Test Kit?
Once you suspect PAP may be causing your patient’s symptoms, request the GM-CSF autoantibody test at no cost to you or your patient. This simple, accurate, and noninvasive autoantibody blood test may help you confirm or rule out aPAP.
This test is designed to provide results as quantitative anti–GM-CSF concentrations. It comes in a compact package with clear, step-by-step instructions.

You can order the test in 1 of 2 forms*:
Serum-based test:
blood tube, then spun to isolate serum.
Dried blood spot test:
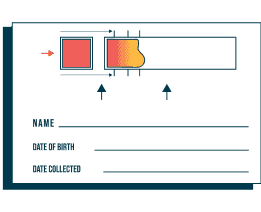
dropped directly onto a collection card.
A high concentration of GM-CSF autoantibodies means your patient has aPAP.
As the ordering physician, you will receive quantitative test results via fax within 7 business days of the completed test arriving at the lab. You may request to have results delivered via email by calling or emailing TrilliumBiO (a CLIA certified lab) using the contact information included in the test kit.
*aPAP ClearPath™ testing is not yet offered in New York State.
Mobile phlebotomy service:

If a serum blood draw is not possible in your office, you can order a dried blood spot test or utilize the aPAP ClearPath™ mobile phlebotomy service. This program allows patients to have their blood drawn in the comfort of their homes.
For more information, contact aPAP@TrilliumBio.com or call 1-888-261-2812, option 3.
References: 1. McCarthy C, Avetisyan R, Carey BC, Chalk C, Trapnell BC. Prevalence and healthcare burden of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2018;13(1):129-133. doi:10.1186/s13023018-0846-y 2. McCarthy C, Kokosi M, Bonella F. Shaping the future of an ultra-rare disease: unmet needs in the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2019;25(5):450-458. doi:10.1097/MCP.0000000000000601 3. Ataya A, Knight V, Carey BC, Lee E, Tarling EJ, Wang T. The role of GM-CSF autoantibodies in infection and autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: a concise review. Front Immunol. 2021;12:752856. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.752856 4. McCarthy C, Carey B, Trapnell BC. Autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022;205(9):1016-1035. doi:10.1164/rccm.202112-2742SO 5. Savara IMPALA-2 study (SAV006-05): IMPALA-2 Investigator Meeting; Savara Inc.; July 2021; Langhorne, PA. 6. McCarthy C, Carey B, Trapnell BC. Blood testing for differential diagnosis of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis syndrome. Chest. 2019;155(2):450-452. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2018.11.002 7. Campo I, Mariani F, Rodi G, et al. Assessment and management of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in a reference center. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2013;8:40-46. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-8-40 8. Data on file. Savara Inc. Investigator’s Brochure. May 28, 2023. 9. Data on file. Savara Inc. 10. Miyashita K, Hozumi H, Inoue Y, Suzuki T, Suda T. Nationwide survey of adult patients with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis using the National Database of designated intractable diseases of Japan. Respir Investig. 2023;61(3):364-370. doi:10.1016/j.resinv.2023.02.011 11. aPAP patient journey & qualitative segmentation; final report. Savara Inc.; 2023; Langhorne, PA. 12. Trapnell BC, Inoue Y, Bonella F, et al.; IMPALA Trial Investigators. Inhaled molgramostim therapy in autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(17):1635-1644. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1913590 13. Carey B, Chalk C, Stock J, et al. A dried blood spot test for diagnosis of autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. J Immunol Methods. 2022;511:113366. doi:10.1016/j.jim.2022.113366 14. Inoue Y, Trapnell BC, Tazawa R, et al., for the Japanese Center of the Rare Lung Diseases Consortium. Characteristics of a large cohort of patients with autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in Japan. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;177(7):752-762. doi:10.1164/rccm.2007081271OC 15. McCarthy C, Bonella F, O'Callaghan M, et al. European Respiratory Society guidelines for the diagnosis and management of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Eur Respir J. 2024;64(5):2400725. doi:10.1183/13993003.00725-2024